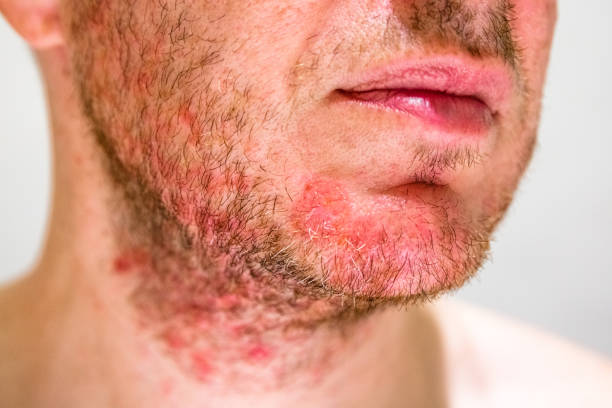
Did you spot a reddish, itchy rash on your skin recently? This could be an indication that you’re contending with folliculitis.
Table Of Contents
−Let’s explore how long folliculitis persists and the potential treatments.
Duration of Folliculitis
Folliculitis, an infection of the hair follicles, varies in duration. Minor cases might resolve within two weeks with appropriate care. Symptoms of conditions like Pseudomonas folliculitis fade in days without medical intervention. However, persistent or severe infections may need prescribed medicines.
If your condition intensifies or lingers, it becomes essential to consult a physician. Adequate care and treatment ensure that minor folliculitis heals without leaving scars.
Understanding Folliculitis
Folliculitis develops when hair follicles become inflamed. Several causes can lead to this skin issue: bacteria, viruses, fungi, or even hair follicle blockages or irritations. Recognizing the different folliculitis types and their treatments can assist in managing this condition efficiently.
Folliculitis Varieties
Folliculitis comes in multiple forms, from mild to intense. Familiar forms encompass Pseudomonas folliculitis, Pityrosporum folliculitis, and bacterial folliculitis. While minor forms may resolve by themselves, persistent or intense infections might necessitate prescription medicines.
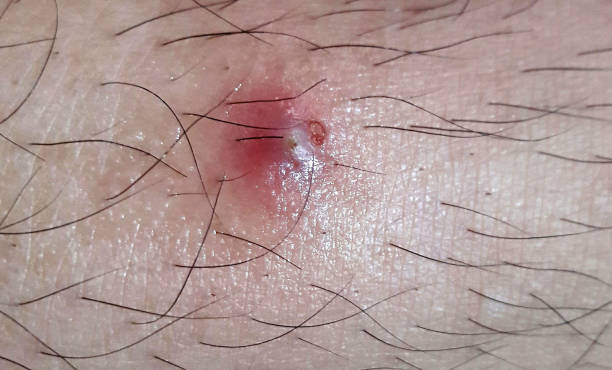
Signs of Folliculitis
This condition, marked by hair follicle inflammation, exhibits a range of symptoms based on its severity.
Typical signs include redness, rashes, tender bumps filled with pus, and discomfort in the affected zone. Some individuals might also experience fever, chills, and tiredness. It’s wise to seek medical advice if you notice these symptoms.
Folliculitis Causes
Several factors contribute to folliculitis. Bacterial infections from agents like staphylococci or propionibacterium acnes are common culprits. Additionally, irritants in pools or hot tubs can cause flare-ups. Physical skin damage, like shaving cuts, can also introduce bacteria, leading to inflammation.
Neglecting folliculitis might escalate the issue, resulting in scars or even permanent hair loss. Addressing any signs of folliculitis promptly is crucial.
Diagnosing Folliculitis
Physicians consider patients’ medical backgrounds and conduct physical checks when diagnosing folliculitis. Sometimes, lesion samples are analyzed to check for bacterial or fungal presence. Occasional imaging tests might also be recommended.
While minor folliculitis might not need intervention, intense cases might necessitate antibiotics or other treatments.
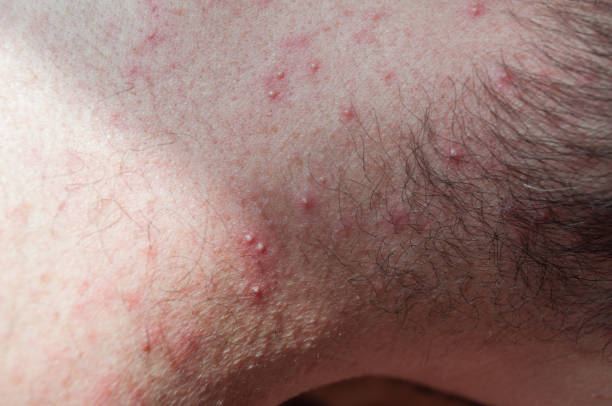
Treatment for Minor Folliculitis
For mild cases, cleanliness and dryness prove beneficial. Avoiding snug outfits and steering clear of pools or hot tubs until healing completes is advisable. Prescribed creams or oral antibiotics might be necessary for stubborn infections. Post-recovery, laser treatments can help reduce any residual dark spots.
Treatment for Severe Folliculitis
Intense forms of folliculitis might need stronger medications, be it antibiotics, antifungals, or antimicrobials. Alongside these, your physician might suggest creams to minimize inflammation. Adhering to medical guidance and maintaining hygiene can aid in swift recovery.
Pseudomonas and Pityrosporum Folliculitis Treatments
Pseudomonas folliculitis responds well to antibiotics. Most individuals find relief within ten days, even without intervention. Nonetheless, consulting a healthcare provider is advised for accurate diagnosis.
For Pityrosporum folliculitis, oral antifungal treatments are common. Patients often see improvements within weeks. Topical antifungals might be used, though they are less effective.
Preventing Folliculitis
Folliculitis prevention hinges on hygiene and proper skin care. Clean, dry skin and loose clothing can lower infection risks. Avoid sharing personal items and consider skipping public pools or hot tubs with high bacterial presence. Addressing underlying skin issues like acne can further help in preventing folliculitis.
Final Thoughts
Folliculitis, while common, varies in severity. Minor cases might be manageable with home remedies, but persistent or intense infections need medical attention. Good hygiene practices, coupled with prompt treatment, can ensure quick recovery and reduce recurrence chances. If you suspect folliculitis, reach out to a medical professional for an evaluation.
Last update on 2024-04-27 / Affiliate links / Images from Amazon Product Advertising API
Affiliate Disclosure: This post contains affiliate links, which means I may receive a small commission, at no extra cost to you, if you make a purchase using these links.

Jay Kang
Just because i'm asian does not mean I don't need shaving. I always wanted to grow a beard when I was young, now I need to shave because hair growth for me is a problem. I'm going through what every man will and has gone through before.





